✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 1474
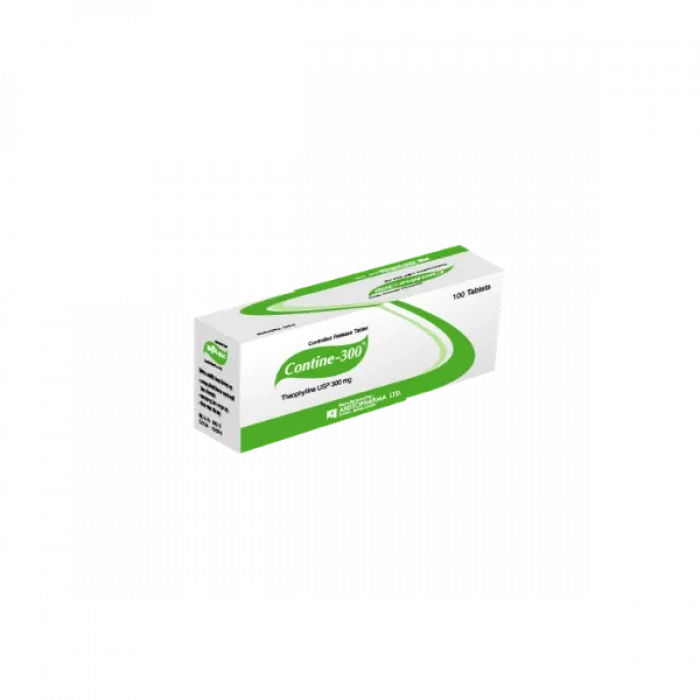
Contine 300mg
Tablet Manufacturer/Distributor: Aristopharma Limited Generic Name: Theophylline 300 mg Tablet
Discount
Price: ৳ 22
MRP:
৳
23.57
5%
Off
✅ Description:
Indications
Contine is indicated for the prevention & treatment of symptoms of asthma and reversible bronchospasm associated with and emphysema.
Pharmacology
Contine (Theophylline) is a bronchodilator, structurally classified as a xanthine derivative. lt has two distinct actions in the airways causes pulmonary reversible obstruction; smooth muscle relaxation and suppression of the response of the airways to stimuli. lt also causes pulmonary vasodilation, stimulates mucociliary clearance and inhibits mast cell mediator release. Theophylline force of contraction increases the of diaphragmatic muscles.
Dosage & Administration
The dose of theophylline must be individualized on the basis of peak serum theophylline concentration measurements in order to achieve a dose that will provide maximum potential benefit with minimal risk of adverse effects. Most of the sustained release preparations may be administered every 12 hours in adults while administration every 8 hours may be necessary in some children with markedly rapid hepatic metabolism of theophylline. The recommended maintenance dose within accepted therapeutic range is as follows:
1-6 months: 10 mg/Kg/day.
6 months-1 year: 12-18 mg/Kg/day
1 year-8 years: 24-24 mg/Kg/day
9-11 years: 16 mg/Kg/day
12 years-15 years: 13 mg/Kg/day
16 years or older: 10 mg/Kg/day (Do not exceed 900 mg/day)
Interactions
Allopurinol, cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, lithium carbonate, oral contraceptive, propranolol when administered increases serum theophylline level concomitantly and rifampicin decreases serum theophylline level.
Contraindications
Theophylline is contraindicated in individuals who have shown hypersensitivity to its components.
Side-Effects
The following side effects have been observed:
Gastro-intestinal: Nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain and diarrhoea. Central nervous system: Headache, irritability, restlessness, insomnia, muscles twitching. Cardiovascular: palpitation, tachycardia, hypotension, circulatory failure.
Respiratory: Tachypnoea.
Renal: Potentiation of diuresis.
Others: Alopecia, hyperglycemia, rash, etc.
=
Pregnancy & Lactation
It is not known whether Theophylline can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Xanthine should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Precautions & Warnings
Various interacting medicines and physiologic circumstances that can affect Theophylline clearance must be carefully considered. Before to starting Theophylline therapy, prior to increasing the Theophylline dose, and throughout follow-up, dosage adjustments are required. The dose of Theophylline used for the commencement of therapy should be low and gradually raised over time if tolerated.
Storage Conditions
Keep all medicines out of reach of children. Store in a cool and dry place, protected from light.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.