✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 7045
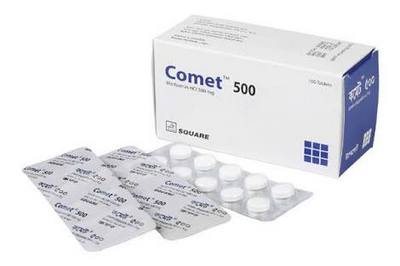
Comet 500mg Tablet
- Used to treat type 2 diabetes in adults and children
- Helps control blood sugar levels
- Available in both quick release and extended-release tablets
- Should be used with caution in patients with liver or kidney disease
- Dosage may need to be adjusted in some patients
- May cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain
- Regular monitoring of kidney and liver function is advisable while taking this medication
Discount
Price: ৳ 48
MRP:
৳
50
5%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery: 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery: 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery: 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-125
Regular Delivery: 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-125
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৫৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৫৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
-
Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
-
Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery: 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery: 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery: 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-125
Regular Delivery: 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-125 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৫৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৫৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে- Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
- Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
✅ Description:
Comet 500mg is a medication that belongs to the biguanide class and is primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes. It works by increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization, lowering hepatic glucose production, and decreasing intestinal glucose absorption. It is available in both quick release and extended-release tablets.
Safety Advices

Alcohol
UNSAFE
It is unsafe to consume alcohol with Comet 500.

Pregnancy
SAFE IF PRESCRIBED
Limited human studies have been conducted on the use of Comet 500 during pregnancy, but it is generally considered safe. Animal studies have shown little to no adverse effects on fetal development.

Breastfeeding
SAFE IF PRESCRIBED
Although limited human data suggests that Comet 500 is likely safe to use during breastfeeding, caution should still be exercised as there is not enough evidence to confirm that the drug does not pose any significant risk to the baby. It is advised to consult with a healthcare professional before taking Comet 500 while breastfeeding.

Driving
CAUTION
Your ability to drive may be affected if your blood sugar is too low or too high. Do not drive if these symptoms occur.

Kidney
CAUTION
Caution should be exercised when using Comet 500 in patients with kidney disease, and dosage adjustment may be necessary. It is not recommended to use Comet 500 in patients with severe kidney disease. Regular monitoring of kidney function tests is advised while taking this medication. It is recommended to consult with a doctor before taking Comet 500.

Liver
CAUTION
Caution is advised when using Comet 500 in patients with liver disease, and dosage adjustment may be necessary. It is recommended to consult with a doctor before taking Comet 500. The medication is typically started with a low dose in patients with mild to moderate liver disease, and is not recommended for use in patients with severe liver disease.
✔️ Indications of Comet 500mg
- Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, especially in overweight people, when food and exercise alone are unable to provide appropriate glycemic control.
- Metformin can be used alone or in conjunction with other oral antidiabetic drugs or insulin in adults.
- Metformin can be taken alone or in conjunction with insulin in children and adolescents as young as ten years old.
- In overweight type 2 diabetes adult patients treated with metformin as first-line treatment following diet failure, there was a decrease in diabetic complications.
✔️ Pharmacology
Metformin is an antihyperglycemic medication of the biguanide class that is used to treat type 2 diabetes. Both baseline and postprandial plasma glucose levels are reduced. It has a different mode of action than sulfonylureas and does not cause hypoglycemia. Metformin increases insulin sensitivity by increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization. It lowers hepatic glucose production, lowers intestinal glucose absorption, and lowers hepatic glucose production.
✔️ Dosage & Administration of Comet 500mg
Comet 500 Dosage:
Metformin Hydrochloride dosage is individualized based on effectiveness and tolerance, without surpassing recommended daily limits.
Adults: Metformin typically begins at 500 mg twice daily or 850 mg once daily with meals. Increase by 500 mg weekly or 850 mg every two weeks, up to 2000 mg daily in divided doses. Glucomin's maximum daily dose is 2550 mg for enhanced glycemic control.
Children start with Metformin 500 mg twice daily, increasing weekly to 2000 mg daily in divided doses.
Metformin extended-release tablets must be swallowed whole, not crushed or chewed.
Adults use Metformin XR 500 mg once daily with dinner, escalating by 500 mg weekly to a max of 2000 mg once daily with dinner, or 1000 mg twice daily with supper if preferred. Patients on Metformin quick-release can shift to Metformin extended-release up to daily max.
Children: Metformin XR hasn't been studied in children.
Kidney impaired: Avoid Metformin if eGFR is below 30 mL/min/1.73 m². Evaluate risks if eGFR drops below 45 mL/min/1.73 m².
✔️ Interaction of Comet 500mg
Carbonic anhydrase (Topiramate, Zonisamide) co-administration may raise the risk of lactic acidosis. Drugs that decrease Metformin clearance (Ranolazine, Dolutegravir, Cimetidine) may cause Metformin buildup. Metformin's effect on lactate metabolism can be amplified by alcohol.
✔️ Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
Any type of acute metabolic acidosis (such as lactic acidosis, diabetic ketoacidosis).
Severe renal failure (GFR <30 mL/min).
Acute conditions with the potential to alter renal function such as dehydration, severe infection, shock.
Acute or chronic disease, which may cause tissue hypoxia such as
- cardiac or respiratory failure,
- recent myocardial infarction,
- shock,
- Hepatic insufficiency,
- acute alcohol intoxication,
- alcoholism.
✔️ Side Effects of Comet 500mg
Hemolytic anemia is a blood and lymphatic system disease that is not well understood.
Metabolism and nutrition disorders:
Very rare:
Lactic acidosis. Decrease of vitamin B12 absorption with a decrease of serum levels during long-term use of metformin. Consideration of such etiology is recommended if a patient presents with megaloblastic anemia. Cases of peripheral neuropathy in patients with vitamin B12 deficiency have been reported in post-marketing experience (frequency not known)
Taste disturbance is a common nervous system disease. Encephalopathy is a condition that is currently unknown.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Very common:
Gastrointestinal disorders, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite. These undesirable effects occur most frequently during the initiation of therapy and resolve spontaneously in most cases. To prevent them, it is recommended that metformin be taken in 2 or 3 daily doses during or after meals. A slow increase of the dose may also improve gastrointestinal tolerability.
Isolated instances of liver function test problems or hepatitis resolving after metformin cessation are extremely rare.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
- Erythema,
- pruritus, and
- urticaria are extremely infrequent.
✔️ Pregnancy & Lactation
Uncontrolled diabetes (gestational or permanent) during pregnancy is linked to an increased risk of congenital malformations and perinatal death. When a patient intends to become pregnant or is pregnant, it is advised that diabetes be managed with insulin rather than metformin to keep blood glucose levels as near to normal as possible, reducing the risk of fetal abnormalities.
Metformin is secreted in human breast milk during breastfeeding. In breastfed newborns/infants, no harmful effects were found. Breastfeeding is not suggested when using metformin since there is insufficient data. The benefits of nursing and the possible danger of harmful effects on the kid should be considered while deciding whether or not to stop breastfeeding.
✔️ Precautions & Warnings for Comet 500mg
Comet 500 is known to be eliminated in large amounts via the kidneys, and the danger of Metformin buildup and lactic acidosis rises as renal function declines. Metformin has been linked to a reduction in vitamin B12 levels.
When combined with insulin or an insulin secretagogue, it raises the risk of hypoglycemia.
✔️ Storage Conditions
Keep the temperature below 30°C and away from light and moisture. Keep out of children's reach.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.