✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 2068
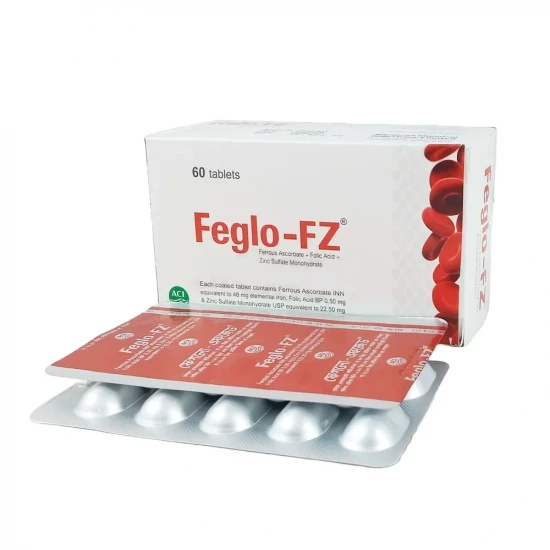
Feglo FZ | 48mg+0.5mg+22.5mg | 1 Strip
Feglo-FZ Tablet | (Ferrous Ascorbate + Folic Acid + Zinc)
- Prophylaxis and treatment of iron deficiency anemia, particularly when dietary intake is insufficient.
- Recommended during pregnancy and lactation, where supplementary iron and zinc are essential.
- Helpful in anemia associated with nutritional deficiencies.
Acute iron toxicity may cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, tarry stools, hematemesis, hypotension, tachycardia, metabolic acidosis, hyperglycemia, dehydration, drowsiness, pallor, cyanosis, seizures, shock, or coma.
Emergency supportive measures are required.
Discount
Price: ৳ 65
MRP:
৳
70
7%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery: 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery: 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery: 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-125
Regular Delivery: 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-125
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৫৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৫৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
-
Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
-
Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery: 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery: 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery: 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-125
Regular Delivery: 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-125 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৫৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৫৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে- Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
- Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
✅ Description:
Ferrous Ascorbate: A stable complex of iron and vitamin C that prevents oxidation and maintains iron in the soluble ferrous form. It enhances absorption and utilization of iron, supporting hemoglobin synthesis and erythropoiesis. Unlike conventional iron salts, this complex resists dissociation in the GI tract, reducing the impact of dietary inhibitors.
Folic Acid: Essential for nucleoprotein synthesis and normal erythropoiesis. It is converted to tetrahydrofolic acid in the body and plays a key role in DNA synthesis, cell division, and neural tube defect prevention during pregnancy.
Zinc: A trace element and cofactor in numerous enzymes. It contributes to DNA synthesis, immune system function, insulin activity, wound healing, and sensory functions (taste and smell).
Together, this combination replenishes iron stores, promotes red blood cell formation, enhances oxygen transport, and improves overall nutritional balance.
✔️ Side Effects:
Usually mild and temporary:
Gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea, constipation, vomiting, diarrhea, epigastric pain, heartburn).
Rare: Allergic reactions to folic acid.
✔️ Dosage & Administration
- Adults & Elderly: 1 tablet daily (before or after meals, absorption is food-independent) or as directed by a physician. In severe cases, dosage may be increased to 2 tablets daily under medical supervision.
- Pediatric use: Safety and efficacy not established.
✔️
Iron reduces absorption of tetracycline antibiotics; separate intake by at least 2 hours.
Absorption of iron may be impaired by penicillamine and antacids.
In renal impairment, prolonged use may increase risk of zinc accumulation.
✔️ Contraindications:
Known hypersensitivity to any component.
Hemolytic anemia or conditions with iron overload (e.g., hemochromatosis, hemosiderosis).
✔️ Pregnancy & Lactation
Use under physician guidance during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
First trimester: Avoid unless iron deficiency is confirmed.
Second and third trimesters: Prophylactic supplementation is justified, especially when zinc is also required.
✔️ Precautions & Warnings
Caution in patients at risk of iron overload (e.g., hemochromatosis, hemolytic anemia, red cell aplasia).
Lack of response to therapy should prompt evaluation for other causes of anemia.
✔️ Storage:
Store below 30°C, in a cool, dry place away from light and moisture.
Keep out of reach of children.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.