✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 3529
Discount
Price: ৳ 96
MRP:
৳
100.7
5%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
🌙 রমযান অফার 🌙
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
-
Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
-
Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে- Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
- Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
🌙 রমযান অফার 🌙
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
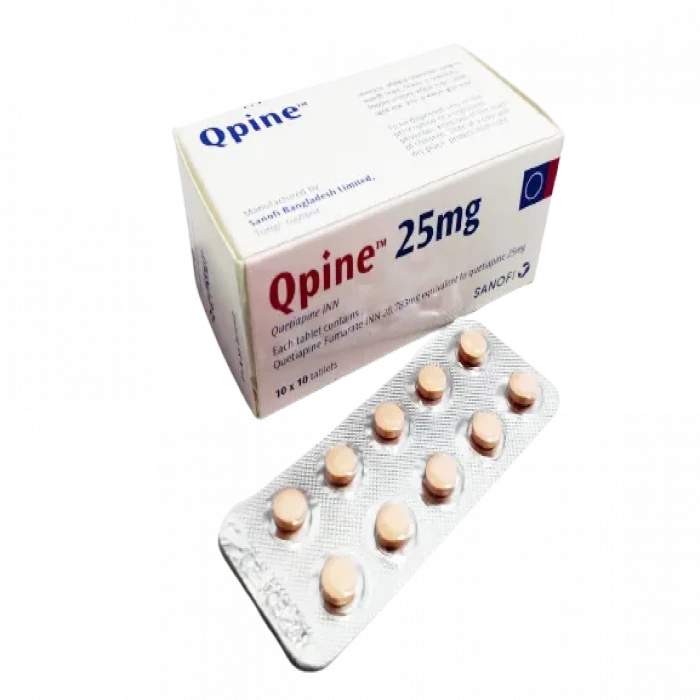
✅ Description:
Indications
Quetiapine is suitable for the treatment of acute and chronic psychosis, including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, including: treatment of manic episodes that meet manic standards related to bipolar disorder and DSMIV, and treatment of depression related to Bipolar disorder Onset, maintenance treatment of bipolar I disorder, combined with mood stabilizers, used to prevent recurrence of mania, depression, or mixed episodes.
Pharmacology
The mechanism of action of quetiapine is the same as that of other drugs that are effective in treating schizophrenia and the acute manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder, but it is unclear. However, it has been suggested that the effect of this drug on schizophrenia is mediated by a combination of antagonism of dopamine type 2 (D2) and serotonin type 2 (5HT2). Antagonism with similar receptor affinity to receptors other than dopamine and 5HT 2 may explain some of the other effects of quetiapine. The antagonism of quetiapine on the histamine H1 receptor may explain the drowsiness observed with this drug. Quetiapine antagonism on the α1 adrenergic receptor may explain the orthostatic hypotension observed with this drug.
Dosage & Administration
Acute and chronic psychoses, including schizophrenia: Quetiapine should be administered twice daily, with or without food. The total daily dose for the first four days of therapy is 50 mg (Day 1), 100 mg (Day 2), 200 mg (Day 3) and 300 mg (Day 4). From Day 4 onwards, the dose should be titrated to the usual effective dose range of 300-450 mg/day. However, this may be adjusted, depending on the clinical response and tolerability of the individual patient, within the range 150 to 750 mg/day.
Manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder: Quetiapine should be administered twice daily, with or without food. The total daily dose for the first four days of therapy is 100 mg (Day 1), 200 mg (Day 2), 300 mg (Day 3) and 400 mg (Day 4). Further dosage adjustments up to 800mg/day by Day 6 should be in increments of no greater than 200 mg/day. The dose may be adjusted depending on clinical response & tolerability of the individual patient, within the range of 200 to 800 mg/day. The usual effective dose is in the range of 400 to 800mg/day.
Depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder: Quetiapine should be administered once daily at bedtime, with or without food. The usual dose is 300 mg/day. The daily dose for the first four days of therapy is 50 mg (Day 1), 100 mg (Day 2), 200 mg (Day 3) and 300 mg (Day 4). Quetiapine can be titrated to 400 mg on Day 5 and up to 600mg by Day 8. Antidepressant efficacy was demonstrated with Quetiapine at 300mg and 600 mg, however no additional benefit was seen in the 600mg group during short term treatment.
Maintenance treatment of bipolar I disorder in combination with mood stabilizers: Patients who have responded to Quetiapine in combination therapy with a mood stabiliser for acute treatment of bipolar disorder should continue on Quetiapine therapy at the same dose. Quetiapine dose can be re-adjusted depending on clinical response and tolerability of the individual patient. Efficacy was demonstrated with Quetiapine (administered twice daily totalling 400mg to 800mg a day) as combination therapy with a mood stabilizer.
Interactions
Caution should be exercised when quetiapine is used at the same time as drugs that are known to cause electrolyte imbalance or increase the QT interval. Co-administration of quetiapine and thioridazine or carbamazepine resulted in an increase in the clearance of quetiapine. The co-administration of quetiapine and phenytoin, another microsomal enzyme inducer, also resulted in an increase in the clearance of quetiapine.
Contraindications
Quetiapine is contraindicated in allergic patients.
Side Effects
The most commonly reported adverse drug reactions (ADRs) for quetiapine are drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, withdrawal symptoms (withdrawal), elevated serum triglyceride levels and elevated total cholesterol (mainly low-density lipoprotein cholesterol), decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, weight gain, reduced hemoglobin, and extrapyramidal symptoms.
Pregnancy & Lactation
The safety and effectiveness of quetiapine during human pregnancy have not been determined. Therefore, quetiapine should be used during pregnancy only if the benefit proves the potential risk, and the dosage and duration of treatment should be as short as possible. The extent to which quetiapine is excreted in human milk is unclear. Therefore, breastfeeding women should be advised to avoid breastfeeding while taking quetiapine.
Precautions & Warnings
Suicide / suicidal thoughts or clinical deterioration: Depression is associated with an increased risk of suicidal thoughts, self-harm, and suicide (suicide-related events). This risk persists until significant relief occurs.
Concomitant diseases: Patients with known cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, or other conditions that can easily cause hypotension should use quetiapine with caution. Quetiapine can cause orthostatic hypotension, especially during initial dose adjustment.
Epilepsy: As with other antipsychotics, caution is advised when treating patients with a history of epilepsy.
Tardive dyskinesia and extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS): If signs and symptoms of tardive dyskinesia occur, consider reducing the dose or discontinuing quetiapine.
Antipsychotic malignant syndrome: This syndrome is related to antipsychotic treatment. Quetiapine should be discontinued and appropriate drug treatment should be given.
Prolonged QT interval: As with other antipsychotics, caution should be exercised when prescribing quetiapine to patients with cardiovascular disease or a family history of prolonged QT interval.
Neutropenia: Severe neutropenia (<0.5x109/L) is rarely reported in clinical trials of quetiapine. Most cases of severe neutropenia occur within the first two months of starting quetiapine.
Hyperglycemia and Diabetes: An increase in blood sugar and hyperglycemia and occasional reports of diabetes have been observed in clinical trials of quetiapine.
Storage Conditions
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the blister pack and the carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month. Store in a cool and dry place away from light.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.