✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 3274
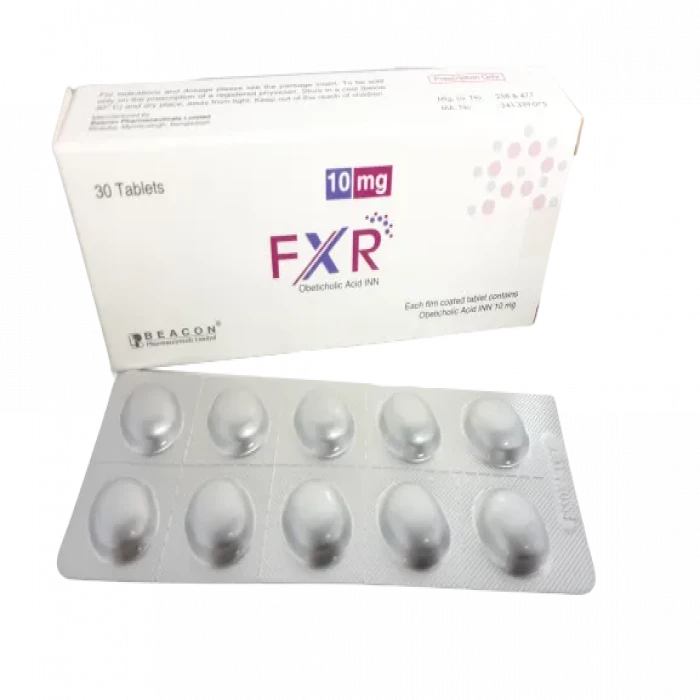
FXR 10mg Tablet 10pcs
Obeticholic Acid 10mg-
- Treats primary biliary cholangitis in adults
Discount
Price: ৳ 528
MRP:
৳
550
4%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
🌙 রমযান অফার 🌙
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
-
Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
-
Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে- Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
- Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
🌙 রমযান অফার 🌙
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
✅ Description:
FXR 10mg Tablet is classified as a Farnesoid X-receptor agonist medication used to treat primary biliary cirrhosis, also known as primary biliary cholangitis. This autoimmune disease damages the bile ducts in the liver, leading to a buildup of bile and liver damage.
FXR 10mg Tablet contains 'Obeticholic acid,' which aids in improving liver function by reducing bile production and accumulation, enhancing bile removal from the liver, and decreasing inflammation, thus treating primary biliary cirrhosis.
Safety Advices

Alcohol
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
Interaction with alcohol is unknown.

Pregnancy
UNSAFE
FXR 10mg Tablet is not recommended for use in pregnant women. Consult your doctor before taking FXR 10mg Tablet.

Breastfeeding
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
It is not known whether FXR 10mg Tablet passes through breast milk. Consult your doctor before taking FXR 10mg Tablet.

Driving
CAUTION
FXR 10mg Tablet has no or negligible influence on your ability to drive or use machines.

Kidney
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
Please consult your doctor if you have kidney impairment or any concerns regarding this.

Liver
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
FXR 10mg Tablet is not recommended for use in patients with complete blockage of the biliary tract (liver, gall bladder, and bile ducts). Consult your doctor before taking FXR 10mg Tablet.
✔️ Uses:
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
✔️ How does FXR 10mg Tablet work?
Obeticholic acid activates the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), which regulates bile acid synthesis, transport, lipid metabolism, and glucose level regulation. By inhibiting bile acid synthesis and increasing bile acid secretion, obeticholic acid reduces the bile acid pool in the liver, preventing its toxic effects and improving liver function.
✔️ Side Effects of FXR 10mg Tablet
The most common side effects of Obeticholic Acid are pruritus, fatigue, and stomach pain and discomfort. Other common adverse effects include rashes, arthralgia (joint pain), oropharyngeal discomfort (pain in the middle of the throat), dizziness, constipation, altered thyroid function, and eczema (skin inflammation).
✔️ Quick Suggestions:
A dietary plan plays a crucial role in managing primary biliary cholangitis. Here are some dietary recommendations for individuals with this condition:
Include the following foods in your diet:
- Bell peppers
- Citrus fruits
- Leafy vegetables
- Tomatoes
- Milk
- Fish
- Low-fat dairy products
- Beans
- Nuts
- Lentils
- Tofu
- Tempeh
It's essential to maintain a healthy, well-balanced diet that emphasizes fruits and vegetables. These foods provide essential nutrients and antioxidants that can support liver health.
- Avoid high-fat and trans-fat foods, as excessive fat intake can strain the liver.
- Minimize the consumption of processed foods, which often contain additives and preservatives that may not be liver-friendly.
- Eliminate or limit the intake of white bread, white pasta, and added sugars. These can lead to weight gain and inflammation.
✔️ Indication
Obeticholic Acid is used to treat primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) in individuals who have not responded well to UDCA, as well as cholestatic liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
✔️ Pharmacology
Obeticholic Acid activates FXR, a nuclear receptor found in the liver and gut. FXR plays a crucial role in regulating bile acid, inflammatory, fibrotic, and metabolic pathways. By reducing de novo cholesterol production and increasing bile acid transport out of hepatocytes, FXR activation decreases intracellular hepatocyte bile acid levels. These actions reduce hepatic bile acid exposure by limiting the total amount of circulating bile acids while increasing choleresis.
✔️ Dosage & Administration of FXR 10mg Tablet
Starting Dosage: The recommended initial dose of Obeticholic Acid is 5 mg orally once daily for adult patients who have not achieved an adequate biochemical response to an appropriate dose of Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA) for at least one year or who are intolerant to UDCA.
Dosage Titration: If an adequate reduction in alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and/or total bilirubin has not been achieved after three months of Obeticholic Acid 5 mg once daily, and the patient tolerates Obeticholic Acid, increase the dose to 10 mg once daily.
Maximum Dosage: The maximum recommended dose of Obeticholic Acid is 10 mg once daily.
Management of Patients with Intolerable Pruritus on Obeticholic Acid: For patients experiencing intolerable pruritus while taking Obeticholic Acid, consider one or more of the following:
- Add an antihistamine or bile acid-binding resin.
- Reduce the dose of Obeticholic Acid to:
- 5 mg every other day for patients intolerant to 5 mg once daily
- 5 mg once daily for patients intolerant to 10 mg once daily
- Temporarily interrupt Obeticholic Acid treatment for up to two weeks, followed by restarting at a reduced dose.
✔️ Interaction
Bile acid binding resins, such as cholestyramine, colestipol, or colesevelam, adsorb and inhibit bile acid absorption, which may reduce Obeticholic Acid absorption, systemic exposure, and efficacy. If taking a bile acid binding resin, administer Obeticholic Acid at least four hours before or after the bile acid binding resin, or at the earliest practicable interval.
Warfarin: Co-administration of Obeticholic Acid and warfarin resulted in a decrease in the International Normalized Ratio (INR). When combining Obeticholic Acid with warfarin, monitor the INR and adjust the warfarin dose as necessary to stay within the target range.
Narrow Therapeutic Index CYP1A2 Substrates: Obeticholic Acid may increase exposure to concomitant CYP1A2 substrates. Therapeutic monitoring is required for CYP1A2 substrates with a limited therapeutic index.
✔️ Contraindications
Obeticholic Acid should not be used by patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug or any of its components, as well as individuals with total biliary obstruction.
✔️ Pregnancy & Lactation
There is insufficient human data on the use of Obeticholic Acid during pregnancy to establish the risk associated with the drug. There is no information on the presence of Obeticholic Acid in human milk, its effects on breastfed infants, or its impact on milk production.
✔️ Precautions & Warnings
Specialized monitoring is necessary for patients with the following clinically significant reactions:
- Severe pruritus
- Reduction in low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C)
✔️ Storage Conditions
Store between 15°C and 30°C in a dry, light-protected place. Keep it out of reach of children.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.