✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 1565
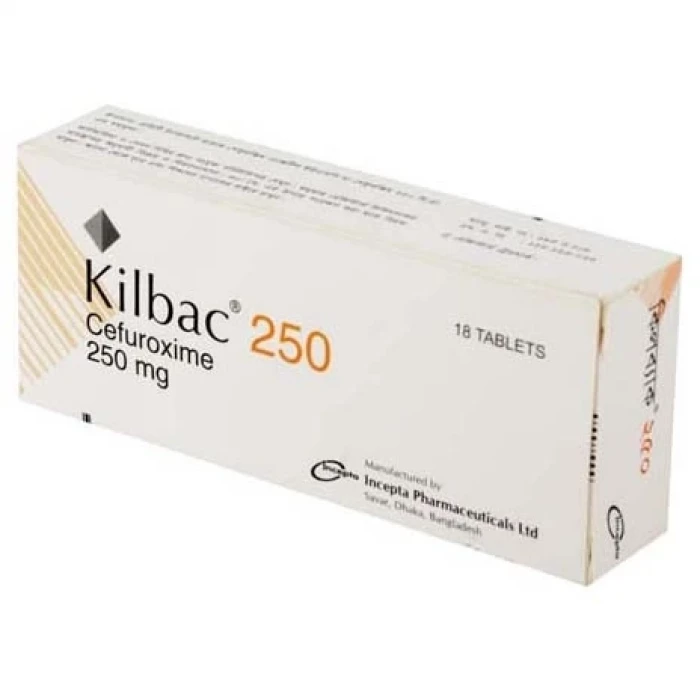
Roximax 250mg (Box)
Generic: Cefuroxime Axetil 250mg
Veritas Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
Discount
Price: ৳ 476
MRP:
৳
501.4
5%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-79
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-79 Regular Delivery - 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.110-125
Regular Delivery - 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.110-125
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৪৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৪৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
-
Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
-
Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-79
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-79 Regular Delivery - 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.110-125
Regular Delivery - 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.110-125 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৪৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৪৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে- Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
- Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
✅ Description:
Roximax is an antibiotic medicine used to treat bacterial infections in your body. It is effective in infections of the lungs (e.g. pneumonia), ear, throat, nasal sinus, urinary tract, skin, soft tissues, bones, and joints. It is also used to prevent infections during surgery. Roximax is given as a drip (intravenous infusion) or as an injection directly into a vein or a muscle under the supervision of a healthcare professional. Your doctor will decide the correct dose for you. You should use this medicine regularly at evenly spaced intervals as per the schedule prescribed by your doctor. Do not skip any doses and finish the full course of treatment even if you feel better. Stopping the medicine too early may lead to the infection returning or worsening. The most common side effects of this medicine include rash, vomiting, diarrhea, increased liver enzymes and nausea. Some people may develop temporary redness or pain at the site of injection. These side effects are usually mild but let your doctor know if they bother you or last more than a few days. Before using it, you should tell your doctor if you are allergic to any antibiotics, and if you have any liver or kidney problems. You should also let your doctor know all other medicines you are taking as they may affect, or be affected by this medicine. Pregnant and breastfeeding mothers should consult their doctor before using it.
Uses of Roximax
- Bacterial infections
Side effects of Roximax
Common
- Rash
- Vomiting
- Allergic reaction
- Increased liver enzymes
- Nausea
- Injection site reaction
- Diarrhea
How to use Roximax
Your doctor or nurse will give you this medicine. Kindly do not self administer.
How Roximax works
Roximax is an antibiotic. It kills bacteria by preventing them from forming the bacterial protective covering (cell wall) which is needed for them to survive.
What if you forget to take Roximax?
If you miss a dose of Roximax, take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular schedule. Do not double the dose.
Quick Tips
- Your doctor has prescribed Roximax to cure your infection and improve your symptoms.
- Do not skip any doses and finish the full course of treatment even if you feel better. Stopping it early may make the infection come back and harder to treat.
- Discontinue Roximax and inform your doctor immediately if you get a rash, itchy skin, swelling of face and mouth, or have difficulty in breathing.
- Diarrhea may occur as a side effect but should stop when your course is complete. Inform your doctor if it does not stop or if you find blood in your stools.
- Avoid consuming alcohol while taking Roximax as it may cause increased side effects.
Brief Description
Indication
Pharyngitis, Acute otitis media, Lyme disease, Susceptible infections, Sinusitis, Otitis media, Skin and skin structure infections,Tonsillitis, Respiratory tract infections, Acute Maxillary Sinusitis, Urinary tract infections, Acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, Surgical Prophylaxis
Administration
Tab: May be taken with or without food. Oral susp: Should be taken with food. IV Preparation Direct injection: reconstitute in 8 mL (for 750-mg vial) or 16 mL (for 1.5-g vial) to obtain ~90 mg/mL solution Infusion: Reconstitute in 100 mL SWI, D5W or NS to obtain 7.5 mg/mL (750-mg vial) or 15 mg/mL (1.5-g vial) solution 7.5 g bulk package not to be used for direct injection IM Preparation Reconstitute 750 mg in 3 mL SWI to obtain ~220 mg/mL solution IV Administration Direct injection: Inject directly into vein over 3-5 minutes or slowly into tubing of free-flowing compatible IV solution Infusion: Infuse intermittently over 15-60 minutes
Adult Dose
Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis 250 mg PO q12hr for 10 days Acute Bacterial Maxillary Sinusitis 250 mg PO q12hr for 10 days Acute Bacterial Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis 250-500 mg PO q12hr for 10 days 500-750 mg IV q8hr; switch to oral therapy as soon as clinically possible Secondary Bacterial Infections of Acute Bronchitis 250-500 mg PO q12hr for 5-10 days Uncomplicated Pneumonia 750 mg IV/IM q8hr Uncomplicated Skin/Skin Structure Infections 250-500 mg PO q12hr for 10 days 750 mg IV/IM q8hr; switch to oral therapy as soon as clinically possible Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections 125-250 mg PO q12hr for 7-10 days 750 mg IV/IM q8hr; switch to oral therapy as soon as clinically possible Gonorrhea Uncomplicated: 1 g PO once or 1.5 g IM once at 2 different sites with 1 g probenecid PO Disseminated: 750 mg IV/IM q8hr Early Lyme Disease 500 mg PO q12hr for 20 days Severe or Complicated Infections 1.5 g IV/IM q8hr; may be administered q6hr in life-threatening situations Oral Susceptible infections Adult: 250 mg bid. Parenteral Susceptible infections Adult: 0.75 g 8 hrly, by deep IM or slow IV inj over 3-5 min or IV infusion, may increase up to 1.5 g 6-8 hrly in more severe infections.
Child Dose
Children: PO 20–30 mg/kg/day q12h For bone and joint infections, up to 100 mg/kg/day IV, IM 100–150 mg/kg/day q8h
Renal Dose
Renal impairment: Patients undergoing haemodialysis should receive an additional 750-mg dose after each dialysis; those undergoing continuous peritoneal dialysis may be given 750 mg bid. CrCl (ml/min) 10-20 750 mg bid. <10 750 mg once daily.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins.
Mode of Action
Cefuroxime binds to one or more of the penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) which inhibits the final transpeptidation step of peptidoglycan synthesis in bacterial cell wall, thus inhibiting biosynthesis and arresting cell wall assembly resulting in bacterial cell death.
Precaution
Severe renal impairment; pregnancy, lactation; hypersensitivity to penicillins. Lactation: Drug excreted in breast milk; use with caution
Side Effect
>10% Diarrhea (4-11%; depends on duration) 1-10% Decreased hemoglobin or hematocrit (10%),Eosinophilia (7%),Nausea or vomiting (3-7%),Vaginitis (<5%),Transient rise in hepatic transaminases (2-4%),Diaper rash (3%),Increase in alkaline phosphatase (2%),Thrombophlebitis (2%),Increase in lactate dehydrogenase (1%) <1% Anemia,Cholestasis,Colitis,Dyspnea,Epidermal necrolysis,Increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine,Jaundice,Nephritis,Prolonged prothrombin time (PT)/international normalized ratio (INR),Rash,Stevens-Johnson syndrome,Stomach cramps,Transient neutropenia and leukopenia,Urticaria Potentially Fatal: Anaphylaxis, nephrotoxicity, pseudomembranous colitis.
Pregnancy Category Note
Pregnancy Available data from published epidemiologic studies, case series, and case reports over several decades in pregnant women have not established drug-associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes Lactation Based on several published case reports describing multiple lactating women receiving therapy via intravenous, intramuscular, and oral routes, drug is present in human milk; the highest maternal milk concentration described occurred in lactating women 8 hours after an intramuscular administration of 750 mg; allowing for an infant milk consumption of 150 mL/kg/day, the estimated breastfed infant dose would be less than 1% of adult dose No data are available on effects of drug on breastfed infant or on milk production; developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for therapy and any potential adverse effects on breastfed infant from drug or from underlying maternal condition
Interaction
May enhance the nephrotoxic effect of strong-acting diuretics (e.g. furosemide) and aminoglycosides. May enhance the effect of oral anticoagulants. May reduce the efficacy of OCs. Probenecid prolongs the excretion of cefuroxime and elevated peak serum level.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.