✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 3927
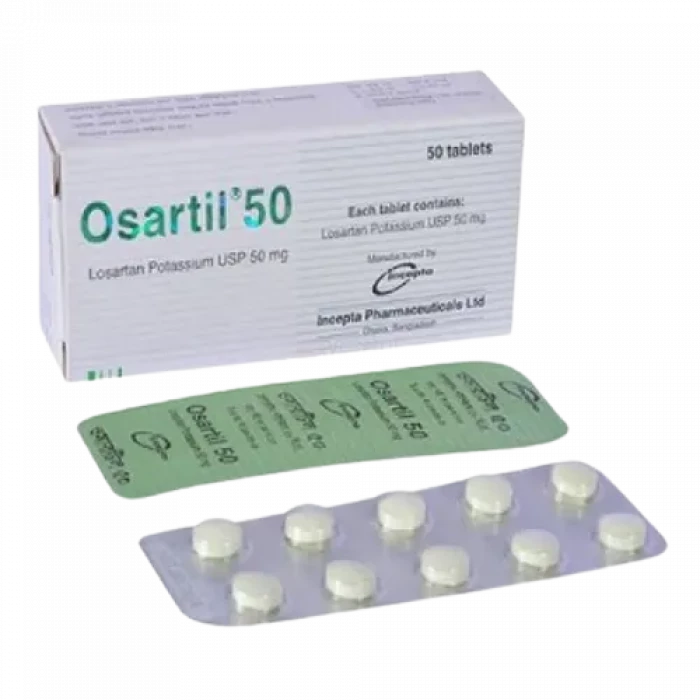
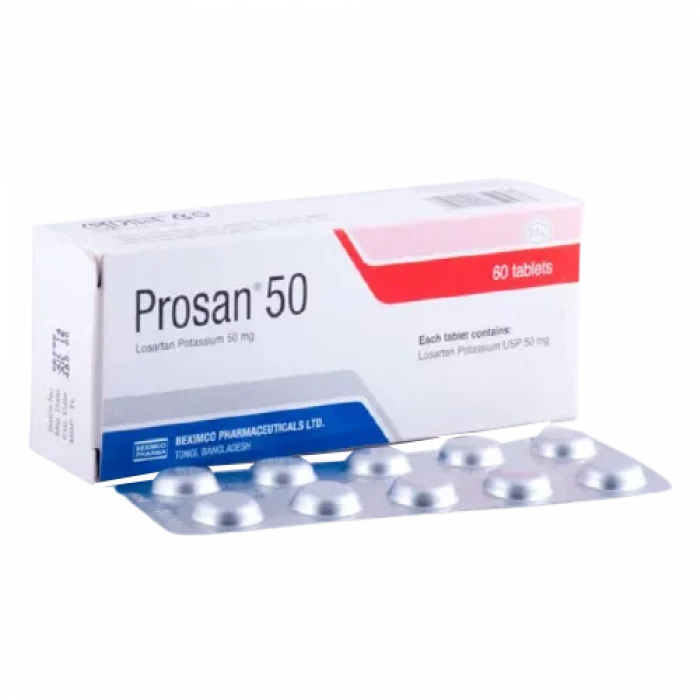
Osartil 50mg Tablet
Losartan Potassium-
- Treats hypertension in adults and children & adolescents (aged 6 to 18 years)
- Protects kidneys in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients
- Treats chronic heart failure in patients (in whom ACE inhibitors become ineffective to treat the disease)
- Reduces risk of stroke (in patients with high blood pressure and thickening of the left ventricle)
Discount
Price: ৳ 95
MRP:
৳
100
5%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
🌙 রমযান অফার 🌙
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
-
Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
-
Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে- Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
- Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
🌙 রমযান অফার 🌙
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
✅ Description:
- Osartil 50mg Tablet contains the active ingredient Losartan, which belongs to a group of medicines called Angiotensin II receptor antagonists. This medication is primarily used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure) in adults and children/adolescents aged 6-18 years.
- Osartil 50mg Tablet also has additional indications. It can be used to protect the kidneys in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients. Furthermore, it is prescribed for patients with chronic heart failure when ACE inhibitors are ineffective in treating the condition. Additionally, Osartil 50mg Tablet may be used to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with high blood pressure and thickening of the left ventricle.
- However, there are certain contraindications and precautions associated with Osartil 50mg Tablet. It is not recommended for use in patients who are allergic to Losartan. Individuals with severely impaired liver function or kidney function should also avoid this medication.
- Before taking Osartil 50mg Tablet, it is important to inform your doctor about any history of angioedema (swelling of the face, lips, throat, and/or tongue). Additionally, if you experience excessive vomiting/diarrhea, have primary hyperaldosteronism (a condition involving increased secretion of the aldosterone hormone), kidney problems, or heart problems (such as heart failure, cardiac arrhythmia, and coronary heart disease), you should notify your doctor.
- Pregnant women should not take Osartil 50mg Tablet, especially after the first trimester (more than 3 months), as it may cause serious harm to the baby. Breastfeeding women should also avoid this medication since it can pass through breast milk.
- Osartil 500mg Tablet is not recommended for use in children under 6 years of age. It should be used with caution in children and adolescents aged 6-18 years. In patients over the age of 75 years, it is advisable to consult a doctor before using this medication.
- The most common side effects of Osartil 50mg Tablet include dizziness, general weakness, tiredness, low blood sugar (with symptoms such as fast heartbeat, shaking, and sweating), changes in kidney function (with symptoms such as decreased urine output, edema, shortness of breath), and anemia. If any of these symptoms worsen, it is important to consult your doctor.
- Please note that this information is not exhaustive, and it is always important to consult a healthcare professional or your doctor for specific advice regarding your medical condition and the use of the Osartil 50mg Tablet.
Safety Advices

Alcohol
UNSAFE
Consumption of alcohol with Osartil 50mg Tablet may increase the risk of low blood pressure and cause adverse effects such as dizziness, fainting, light-headedness, or headache.

Pregnancy
UNSAFE
Osartil 50mg Tablet is unsafe for use during pregnancy as it can cause harm to your developing fetus.

Breastfeeding
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
Osartil 50mg Tablet is not recommended during breastfeeding. It is advisable to consult a doctor to find a safer alternative.

Driving
UNSAFE
Avoid driving vehicles or operating machines if you feel dizzy or drowsy after taking Osartil 50mg Tablet.

Kidney
CAUTION
Osartil 50mg Tablet should be given with caution, especially if you have a history of Kidney diseases/conditions. The dose may be adjusted by your doctor as required.

Liver
CAUTION
Osartil 50mg Tablet should be given with caution, especially if you have a history of Liver diseases/conditions. The dose may be adjusted by your doctor as required.
✔️ Uses of Osartil 50mg Tablet
- Hypertension
- Diabetic Nephropathy
- Hypertension with left ventricular hypertrophy
✔️ How does Osartil 50mg Tablet work?
Osartil 50mg Tablet blocks the action of a chemical messenger that causes the narrowing of the blood vessels. Hence, it relaxes the blood vessels and allows the blood to flow easily, thus lowering blood pressure.
✔️ Side Effects of Osartil 50mg Tablet
- Stomach discomfort
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Edema
- Chest Pain
- Nasal congestion
- Decreased blood pressure
- Hypoglycemia (low blood glucose level)
- Increased potassium level in the blood
- Increased blood urea
- and upper respiratory infections are the most prevalent adverse effects.
✔️ Quick Suggestions:
- Take the medication at the same time every day to help you remember.
- Be cautious of dizziness, especially during the first few days. Rise slowly if you have been sitting or lying down for an extended period.
- Your doctor may conduct regular tests to monitor urea, creatinine, and potassium levels in your blood.
- Maintain a low-salt diet and limit processed food intake as they are often high in sodium. Replace salt with herbs and spices for flavoring.
- Engage in regular exercise, such as cycling, walking, jogging, dancing, or swimming, for a minimum of 30 minutes per day.
- Avoid stress triggers and find time for relaxation and activities you enjoy to manage chronic stress.
- Follow a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products.
- Refrain from smoking and consuming alcohol.
- Monitor your blood pressure regularly, and if you notice any fluctuations, consult your doctor.
- Along with Osarti 50mg Tablet, maintaining a low-salt diet and regular exercise are recommended for optimal results.
- Consult your doctor before taking anti-inflammatory medicines like ibuprofen alongside Osartil 50mg Tablet.
- Do not take Osartil 50mg Tablet if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Do not discontinue the medication suddenly without consulting your doctor.
✔️ Indication
Osartil 50mg Tablet is used to lower high blood pressure and protect the kidneys from diabetes. It reduces the risk of stroke by relaxing blood vessels and lowering blood pressure.
✔️ Pharmacology
Losartan Potassium is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) and belongs to a class of medications that inhibit the action of angiotensin II on its receptors. Unlike previous ARBs, Losartan Potassium is not a peptide but a non-peptide compound. It selectively binds to the angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor, which is found in various tissues, including vascular smooth muscle, the adrenal glands, the kidneys, and the heart.
By blocking the AT1 receptor, Losartan Potassium prevents the binding of angiotensin II and inhibits its vasoconstrictive effects. This leads to relaxation of the blood vessels, resulting in vasodilation and a decrease in blood pressure. Additionally, Losartan Potassium reduces the production and release of aldosterone, a hormone that promotes sodium and water retention, thereby further contributing to its antihypertensive effects.
Overall, Losartan Potassium helps to lower blood pressure and is used in the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure) and certain conditions related to the heart and blood vessels. It is important to take Losartan Potassium as prescribed by a healthcare professional and to follow their instructions for optimal therapeutic benefits.
✔️ Dosage & Administration of Osartil 50mg Tablet
The usual starting and maintenance dose for most patients is 50 mg once daily. If the desired antihypertensive effect is not achieved with 50 mg once daily, a dose of 25 mg twice daily may be considered before increasing the dose further.
For patients who are intravascular volume-depleted, such as those receiving high-dose diuretics, a lower starting dose of 25 mg once daily is recommended.
The total daily dose of Losartan Potassium can range from 25 mg to 100 mg, depending on the individual patient's response and the prescribing physician's judgment. The dose can be administered once daily or divided into two doses taken twice daily.
✔️ Interaction
Rifampicin and fluconazole can reduce the levels of the active metabolite of Losartan Potassium. It is important to inform your doctor if you are taking these medications concurrently with Losartan Potassium.
Concurrent use of Losartan Potassium with hydrochlorothiazide, a diuretic, may result in an enhanced antihypertensive effect. This combination should be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Concurrent use of Losartan Potassium with potassium-sparing diuretics (such as spironolactone, triamterene, amiloride), potassium supplements, or potassium-containing salt substitutes may lead to an increase in serum potassium levels. Regular monitoring of potassium levels is recommended in such cases.
The nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug indomethacin may reduce the antihypertensive effect of Losartan Potassium. If you are taking indomethacin or any other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, it is important to inform your doctor.
Concurrent use of an ACE inhibitor (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor), an angiotensin receptor antagonist (such as Losartan Potassium), an anti-inflammatory medication, and a thiazide diuretic can increase the risk of renal impairment. Close monitoring of renal function is necessary when using these medications together.
✔️ Contraindications
Losartan Potassium is not recommended for use in pregnant women due to the potential risk of harm to the unborn baby (fetus). It is important for pregnant women to consult with their healthcare provider for alternative treatment options.
Additionally, Losartan Potassium should not be used in individuals who are allergic to any of its components.
In diabetic individuals, the use of Losartan Potassium with Aliskiren, another medication used to treat high blood pressure, is generally not recommended. This combination may increase the risk of certain side effects, including low blood pressure, high potassium levels, and changes in kidney function. It is important to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking, including any over-the-counter drugs or supplements, to ensure safe and effective treatment.
✔️ Pregnancy & Lactation
Losartan Potassium is actually classified as Pregnancy Category D in the second and third trimesters and Pregnancy Category C in the first trimester.
Pregnancy Category D means that there is positive evidence of fetal risk based on human data, but the potential benefits of the medication may outweigh the risks in certain situations. Losartan Potassium should generally be avoided during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy due to the risk of harm to the unborn baby, including reduced kidney function, low amniotic fluid levels, developmental abnormalities, and even death.
In the first trimester, Losartan Potassium is classified as Pregnancy Category C, which means that there are no well-controlled studies on pregnant women, and the potential benefits and risks should be carefully considered before using the medication during this period.
Regarding breastfeeding, it is unknown if Losartan Potassium is excreted in human milk. However, many medications are known to be excreted in breast milk. Therefore, a decision should be made whether to discontinue breastfeeding or discontinue the use of Losartan Potassium, taking into consideration the importance of the medication for the mother's health.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as your doctor or obstetrician, if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, as they can provide the most appropriate guidance regarding the use of Losartan Potassium or alternative medications for your specific situation.
✔️ Precautions & Warnings
- Inform your doctor if you have diabetes, kidney problems, or liver problems before taking Osartil 50mg Tablet.
- Pregnant women, especially in the second and third trimesters, should avoid taking Osartil 50mg Tablet as it may harm the unborn baby (fetus). Consult a doctor before using the medication if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Avoid consuming alcohol while taking Osartil 50mg Tablet as it can increase the risk of low blood pressure.
- Do not take potassium supplements along with Osartil 50mg Tablet as it may result in high potassium levels in the blood.
- Regular blood tests and blood pressure monitoring are recommended while using Osartil 50mg Tablet.
✔️ Storage Conditions
Keep away from light and heat in a dry area. Keep out of children's reach.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.