✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 6616
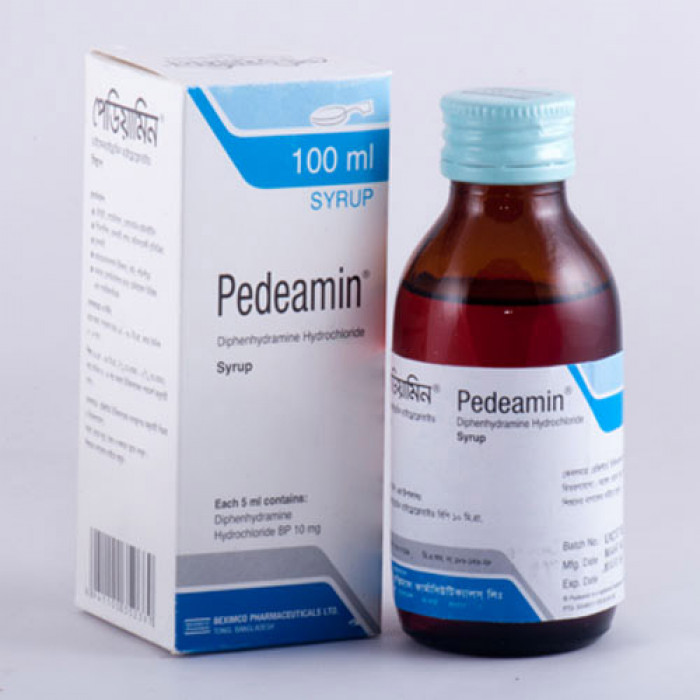
Pedeamin Syrup
- Diphenhydramine is classified as a first-generation antihistamine, and one of its notable side effects is sedation. It readily crosses the blood-brain barrier, which can cause drowsiness and sedation. For this reason, diphenhydramine is often used as a sleep aid in over-the-counter sleep medications.
- Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride is an antihistamine medication commonly used to relieve symptoms associated with allergies, such as sneezing, itching, watery eyes, and runny nose. It works by blocking the effects of histamine, a substance in the body that causes allergic symptoms.
Discount
Price: ৳ 43
MRP:
৳
45
5%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery: 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery: 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery: 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-125
Regular Delivery: 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-125
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৫৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৫৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
-
Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
-
Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery: 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery: 24-48 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery: 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-125
Regular Delivery: 48-96 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-125 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৫৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৫৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে- Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
- Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
✅ Description:
Pedeamin Syrup is indeed an antihistamine medication used to relieve symptoms associated with allergies, hay fever, and the common cold. It can effectively alleviate symptoms such as rash, itching, watery eyes, itchy eyes/nose/throat, cough, runny nose, and sneezing by blocking the action of histamine, a natural substance produced by the body during an allergic reaction.
Additionally, Pedeamin Syrup is commonly used to prevent and treat symptoms of motion sickness, including nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. Its ability to block another natural substance called acetylcholine contributes to its drying effects, reducing symptoms like watery eyes and runny nose.
It's important to note that cough-and-cold products containing diphenhydramine are generally not recommended for children under 6 years of age unless specifically directed by a doctor. Long-acting tablets or capsules may not be suitable for children under 12 years of age. It's essential to follow the specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider or the product's packaging when using diphenhydramine or any other medication.
Furthermore, it is crucial to use cough-and-cold products with caution and adhere to proper dosage directions to minimize the risk of serious side effects. It's important not to use diphenhydramine or similar medications to induce sleep in children. Avoid giving multiple cough-and-cold medications that contain the same or similar ingredients simultaneously to prevent potential overdose. It is advisable to consult a doctor or pharmacist for alternative ways to relieve coughs and cold symptoms, such as staying hydrated, using a humidifier, or using saline nose drops or spray.
Safety Advices

Alcohol
UNSAFE
Pedeamin is generally considered safe to use during pregnancy. Animal studies have shown low or no adverse effects on the developing baby; however, there are limited human studies.

Pregnancy
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
Pedeamin Syrup is generally considered safe to use during pregnancy. Animal studies have shown low or no adverse effects on the developing baby; however, there are limited human studies.

Breastfeeding
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
Pedeamin Syrup is probably safe to use during breastfeeding. Limited human data suggests that the drug does not represent any significant risk to the baby. Larger doses or prolonged use of Pedeamin may cause sleepiness and other effects in the baby

Driving
UNSAFE
Pedeamin Syrup may decrease alertness, affect your vision or make you feel sleepy and dizzy. Do not drive if these symptoms occur.

Kidney
SAFE IF PRESCRIBED
Pedeamin Syrup is safe to use in patients with kidney disease. No dose adjustment of Pedeamin is recommended. However, talk to your doctor if you have any underlying kidney disease.

Liver
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
There is limited information available on the use of Pedeamin Syrup in patients with liver disease. Please consult your doctor.
✔️ Uses of Pedeamin Syrup
- Treat Allergies
✔️ How does Pedeamin Syrup work?
Pedeamin is an antihistaminic medication. It blocks the action of certain chemical messengers that are responsible for inflammation, congestion, itching, and other allergic reactions.
✔️ Side Effects of Pedeamin Syrup
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Nervousness
- Stomach pain
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Insomnia (difficulty in sleeping)
- Impaired coordination
- Headache
- Sedation
- Inability to concentrate
- Irritability
- Tremors
- Dryness in mouth
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Constipation
✔️ Quick Suggestions:
✔️ Indication
Pedeamin Syrup is used-
- Vasomotor rhinitis can be seasonal or permanent.
- Angioneurotic edema, urticaria, and anaphylaxis
- Pruritic symptoms
- Emesis and motion sickness medicine
- Meniere's illness and Parkinsonism are two examples.
✔️ Pharmacology
Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine that also acts as an anticholinergic and sedative. It competes with histamine for H1-receptor sites on effector cells in the GI tract, blood arteries, and lungs.
✔️ Dosage & Administration of Pedeamin Syrup
It's important to note that these dosages are general guidelines, and individual dosing may vary based on factors such as age, weight, medical condition, and other medications being taken. Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Shake well before use is always best to consult a healthcare professional or follow the instructions provided by a doctor or pharmacist for personalized dosing recommendations.
For adults:
- Allergic conditions and motion sickness treatment: The usual dose is 25-50 mg taken orally 3-4 times daily. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 300 mg.
- Prevention of motion sickness: Take 30 minutes before exposure to motion.
- Parkinson's disease: The initial dose is usually 25 mg taken three times daily, which may be increased to 50 mg four times daily if necessary.
- Short-term management of insomnia: Take 50 mg 30 minutes before bedtime as needed.
For children:
- Allergic reaction: The dosage varies based on age. For children aged 2-6 years, the dose is 6.25 mg every 4-6 hours, not exceeding 37.5 mg per day. For children aged 6-12 years, the dose is 12.5-25 mg every 4-6 hours, not exceeding 150 mg per day. For children older than 12 years, the dose is 25-50 mg every 4-6 hours, not exceeding 300 mg per day.
- Occasional insomnia: For children older than 12 years, the dose is 50 mg taken 30 minutes before bedtime.
- Cough: The safety and efficacy of diphenhydramine for cough in children have not been established.
- Motion sickness: For children older than 12 years, the dose is 12.5-25 mg every 6-8 hours or 150 mg/m², not exceeding 300 mg per day. Administer 30 minutes before motion.
For individuals with renal impairment, no dosage adjustment is typically needed, as diphenhydramine does not undergo significant renal elimination.
✔️ Interaction
Decreased absorption of para-aminosalicylic acid (PAS): Diphenhydramine can significantly reduce the gastrointestinal absorption of para-aminosalicylic acid, an antituberculous drug. It is important to separate the administration of diphenhydramine and PAS by a sufficient time interval to avoid this interaction. Your healthcare provider should provide specific instructions regarding the timing of these medications.
Sedative effect with CNS depressants: Diphenhydramine is a sedating antihistamine, and its sedative effect can be enhanced when used in combination with other central nervous system (CNS) depressants. Examples of CNS depressants include alcohol, tranquilizers, sedatives, and certain antidepressants. Using diphenhydramine with these substances can increase drowsiness and impair cognitive and motor functions. It is advisable to avoid or use caution when combining diphenhydramine with other CNS depressants.
Anticholinergic interactions: Diphenhydramine has anticholinergic properties, which means it blocks the action of acetylcholine in the body. Other medications with anticholinergic effects can potentially amplify the anticholinergic adverse effects of diphenhydramine. This can lead to symptoms such as dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary retention, constipation, and confusion. If you are taking other medications with anticholinergic effects, it's important to discuss this with your healthcare provider to assess the potential risks and benefits.
✔️ Contraindications
Ammonium chloride is contraindicated in the presence of known hypersensitivity to Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride. It is also contraindicated in the presence of compromised hepatic or renal function.
✔️ Pregnancy & Lactation
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is classified as a Category B medication for use during pregnancy. Category B means that there are no well-controlled studies in pregnant women, but animal studies have not shown any adverse effects on the fetus. However, as a precautionary measure, diphenhydramine hydrochloride should only be taken during pregnancy when it is deemed absolutely necessary and the potential benefits outweigh the potential risks.
Regarding breastfeeding, diphenhydramine hydrochloride is excreted in breast milk. Therefore, it is generally advised to avoid using diphenhydramine hydrochloride while breastfeeding to prevent potentially adverse effects on the infant.
It's crucial to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice regarding the use of diphenhydramine hydrochloride during pregnancy or while breastfeeding. They will be able to assess your specific situation and provide you with the most appropriate recommendations.
✔️ Precautions & Warnings
- Epilepsy: Diphenhydramine may lower the seizure threshold and can potentially increase the risk of seizures in individuals with epilepsy. Caution should be exercised when using diphenhydramine in such cases.
- Elderly: Elderly individuals may be more susceptible to the sedative and anticholinergic effects of diphenhydramine. It is recommended to use caution and adjust the dosage accordingly in this population.
- Performing tasks requiring mental alertness: Diphenhydramine can cause drowsiness and impair cognitive function. Individuals taking this medication should avoid activities that require mental alertness, such as driving or operating heavy machinery.
- Angle-closure glaucoma: Diphenhydramine can cause pupillary dilation, which may precipitate an acute angle-closure glaucoma attack in susceptible individuals. It is contraindicated in individuals with known or suspected angle-closure glaucoma.
- Pyroduodenal obstruction and urinary tract obstruction: Diphenhydramine may worsen these conditions due to its anticholinergic effects. It is contraindicated in individuals with these obstructions.
- Hyperthyroidism: Diphenhydramine can have effects on the cardiovascular system, including tachycardia and increased blood pressure. Caution should be exercised in individuals with hyperthyroidism.
- Raised intraocular pressure: Diphenhydramine can increase intraocular pressure. It should be used with caution in individuals with conditions predisposing them to raised intraocular pressure, such as narrow-angle glaucoma.
- Cardiovascular disease: Diphenhydramine can have effects on the cardiovascular system, including changes in heart rate and blood pressure. Caution should be exercised in individuals with cardiovascular disease.
- Acute asthma: Diphenhydramine may thicken respiratory secretions and impair expectoration, potentially worsening symptoms in individuals with acute asthma. It should be used with caution in such cases.
- Pregnancy and lactation: Diphenhydramine is known to cross the placenta and enter breast milk. It is generally not recommended during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, and is contraindicated during breastfeeding due to potential adverse effects on the infant.
✔️ Storage Conditions
- Store Syrup below 30°C in a cool and dry place.
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children and pets.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.