✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 2578
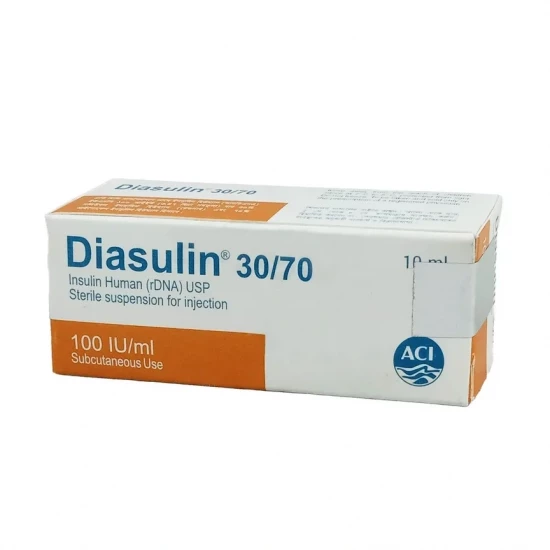
Diasulin 30/70 Vial | 100IU/ml
Diasulin Injection (Human Insulin rDNA)
Therapeutic Class: Antidiabetic – Human Insulin
Dosage Form: Suspension for Injection
Available Formulations:
- Diasulin 30/70: 30% Regular Insulin + 70% Isophane Insulin
- Diasulin 50/50: 50% Regular Insulin + 50% Isophane Insulin
Discount
Price: ৳ 410
MRP:
৳
418
2%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
🌙 রমযান অফার 🌙
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
-
Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
-
Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে- Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
- Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
🌙 রমযান অফার 🌙
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
✅ Description:
Diasulin is indicated for:
- Management of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus inadequately controlled by diet and/or oral antidiabetic agents
- Initial stabilization of diabetes during episodes such as diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar non-ketotic syndrome, or stress conditions (e.g., severe infections, major surgery)
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
✔️ Pharmacology
Diasulin (Human Insulin rDNA) lowers blood glucose by promoting glucose uptake into muscle and fat cells and inhibiting hepatic glucose output.
Onset of action: ~30 minutes
Peak plasma level: 1–3 hours
Duration of action: 18–24 hours
Insulin has a very short plasma half-life and does not significantly bind to plasma proteins.
✔️ Composition
30/70 formulation:
Each ml contains Insulin Human (rDNA) USP 100 IU = 30% Regular Insulin + 70% Isophane Insulin.
50/50 formulation:
Each ml contains Insulin Human (rDNA) USP 100 IU = 50% Regular Insulin + 50% Isophane Insulin.
✔️ Dosage & Administration
The dosage is individualized according to patient requirements.
Typical maintenance dose (Type 1 Diabetes):
0.5–1.0 IU/kg/day (in divided doses)
Children (pre-pubertal): 0.7–1.0 IU/kg/day
Type 2 Diabetes (initial): 0.3–0.6 IU/kg/day
Note: Each injection should be followed within 30 minutes by a carbohydrate-containing meal or snack.
রেজিস্টার্ড চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন।
✔️ Side Effects
Most common: Hypoglycemia (dose-related)
Local effects: Lipodystrophy at the injection site
Systemic hypersensitivity: Rash, itching, angioedema, breathing difficulty, hypotension (rare but serious)
Transient edema may occur at therapy initiation.
✔️ Administration Instructions
Administer subcutaneously, preferably in the abdominal wall, thigh, gluteal, or deltoid region.
Rotate injection sites within the same area to prevent lipodystrophy.
Abdominal injections ensure faster absorption.
Before use, gently mix the suspension by rolling the cartridge between the hands until uniformly white and cloudy.
Do not use if frozen, discolored, or with clumps or solid particles.
Always remove the needle after injection to prevent leakage and potency loss.
✔️ Insulin dosage may require adjustment during:
- Illness, infection, or fever (↑ requirement)
- Renal or hepatic impairment (↓ requirement)
- Changes in physical activity or diet
- Transition to a different insulin formulation
✔️ Drug Interactions
May decrease insulin requirement:
Oral hypoglycemics, MAOIs, ACE inhibitors, non-selective beta-blockers, salicylates, alcohol
May increase insulin requirement:
Thiazides, corticosteroids, thyroid hormones, beta-sympathomimetics, growth hormone, danazol
Caution:
Beta-blockers may mask symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Alcohol may prolong or intensify hypoglycemia.
✔️ Use in Pregnancy & Lactation
- Insulin does not cross the placenta; safe during pregnancy.
- Insulin requirements decrease in the first trimester and increase in later stages.
- After delivery, insulin needs return to pre-pregnancy levels.
- Safe for lactating mothers, but dosage adjustment may be necessary.
✔️ Precautions & Warnings
- Inadequate dosing or discontinuation may cause hyperglycemia or ketoacidosis (life-threatening in Type 1 diabetes).
- Overdosage may cause hypoglycemia—manage with glucose or glucagon as appropriate.
- Switching between insulin types or brands should be done under medical supervision.
- Before long travel or a time-zone change, consult a physician for dosage timing adjustments.
✔️ Contraindications
Hypoglycemia
Hypersensitivity to human insulin or any excipient
✔️ Precautions & Warnings
Mild hypoglycemia: Treat with oral glucose or sugar.
Severe hypoglycemia: Treat with Glucagon (0.5–1 mg IM/SC) or IV glucose; follow with oral carbohydrate intake after recovery to prevent relapse.
✔️ Storage Conditions
- Store between 2°C and 8°C (refrigerated). Do not freeze.
- Keep in outer carton to protect from light.
- In-use cartridge:
- Up to 6 weeks below 25°C, or
- Up to 4 weeks below 30°C.
- Always mix thoroughly before use by rolling gently between palms.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.